15.网络通信-通信必备知识-序列化和反序列化2进制数据-序列化
15.1 知识点
非字符串类型转字节数组
- 关键类:BitConverter
- 所在命名空间:System
- 主要作用:除字符串的其它常用类型和字节数组相互转换
//把int型的1转换成字节数组
byte[] byteArray1 = BitConverter.GetBytes(1);
字符串类型转字节数组
- 关键类:Encoding
- 所在命名空间:System.Text
- 主要作用:将字符串类型和字节数组相互转换,并且决定转换时使用的字符编码类型,网络通信时建议大家使用UTF-8类型
//转换字符串人间自有韬哥在
byte[] byteArray2 = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("人间自有韬哥在");
如何将一个类对象转换为二进制
- 注意:网络通信中我们不能直接使用数据持久化2进制知识点中的
- BinaryFormatter 2进制格式化类
- 因为客户端和服务器使用的语言可能不一样,BinaryFormatter是C#的序列化规则,和其它语言之间的兼容性不好
- 如果使用它,那么其它语言开发的服务器无法对其进行反序列化
- 我们需要自己来处理将类对象数据序列化为字节数组
声明测试类对象
public class PlayerInfo
{
public int lev;
public string name;
public short atk;
public bool sex;
}
将类对象转换成字节数组
//单纯的转换一个变量为字节数组非常的简单
//但是我们如何将一个类对象携带的所有信息放入到一个字节数组中呢
//我们需要做以下几步
//1.明确 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组 的容量(注意:在确定字符串字节长度时要考虑解析时如何处理)
PlayerInfo playerInfo = new PlayerInfo();
playerInfo.lev = 10;
playerInfo.name = "韬老狮";
playerInfo.atk = 88;
playerInfo.sex = false;
//得到的 这个Info数据 如果转换成 字节数组 那么字节数组容器需要的容量
int indexNum = sizeof(int) + //lev int类型 4
sizeof(int) + //代表 name字符串转换成字节数组后 name数组的长度 4
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(playerInfo.name).Length + //name字符串具体字节数组的长度
sizeof(short) + //atk short类型 2
sizeof(bool); //sex bool类型 1
//2.申明一个 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器
byte[] playerBytes = new byte[indexNum];
//3.将对象中的所有信息转为字节数组并放入 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器 中(可以利用数组中的CopeTo方法转存字节数组)
//CopyTo方法的第二个参数代表 从容器的第几个位置开始存储
int index = 0;//从 playerBytes数组中的第几个位置去存储数据
//等级 把等级转成字节数组 拷贝到 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器
BitConverter.GetBytes(playerInfo.lev).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);//索引加上对应字节
//姓名 姓名长度是不固定的 所以要先存姓名长度 用int来存
byte[] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(playerInfo.name);
int num = strBytes.Length;//姓名占多少字节
//存储的是姓名转换成字节数组后 字节数组的长度
BitConverter.GetBytes(num).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);//索引加上对应字节
//存储字符串的字节数组 真正的存入姓名
strBytes.CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += num;//存入姓名后加上索引
//攻击力 把攻击力转成字节数组 拷贝到 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器
BitConverter.GetBytes(playerInfo.atk).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(short);//索引加上对应字节
//性别 把性别转成字节数组 拷贝到 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器
BitConverter.GetBytes(playerInfo.sex).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(bool);//索引加上对应字节
可以在类对象封装转换方法
public byte[] GetBytes()
{
int indexNum = sizeof(int) + //lev int类型 4
sizeof(int) + //代表 name字符串转换成字节数组后 数组的长度 4
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(name).Length + //字符串具体字节数组的长度
sizeof(short) + //atk short类型 2
sizeof(bool); //sex bool类型 1
byte[] playerBytes = new byte[indexNum];
int index = 0;//从 playerBytes数组中的第几个位置去存储数据
//等级
BitConverter.GetBytes(lev).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
//姓名
byte[] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(name);
int num = strBytes.Length;
//存储的是姓名转换成字节数组后 字节数组的长度
BitConverter.GetBytes(num).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
//存储字符串的字节数组
strBytes.CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += num;
//攻击力
BitConverter.GetBytes(atk).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(short);
//性别
BitConverter.GetBytes(sex).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(bool);
return playerBytes;
}
总结
我们对类对象的2进制序列化主要用到的知识点是
- BitConverter转换非字符串的类型的变量为字节数组
- Encoding.UTF8转换字符串类型的变量为字节数组(注意:为了考虑反序列化,我们在转存2进制,序列化字符串之前,先序列化字符串字节数组的长度)
转换流程是
- 明确字节数组的容量
- 申明一个装载信息的字节数组容器
- 将对象中的所有信息转为字节数组并放入该容器当中(利用数组中的CopeTo方法转存字节数组)
15.2 知识点代码
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerInfo
{
public int lev;
public string name;
public short atk;
public bool sex;
public byte[] GetBytes()
{
int indexNum = sizeof(int) + //lev int类型 4
sizeof(int) + //代表 name字符串转换成字节数组后 数组的长度 4
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(name).Length + //字符串具体字节数组的长度
sizeof(short) + //atk short类型 2
sizeof(bool); //sex bool类型 1
byte[] playerBytes = new byte[indexNum];
int index = 0;//从 playerBytes数组中的第几个位置去存储数据
//等级
BitConverter.GetBytes(lev).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
//姓名
byte[] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(name);
int num = strBytes.Length;
//存储的是姓名转换成字节数组后 字节数组的长度
BitConverter.GetBytes(num).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
//存储字符串的字节数组
strBytes.CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += num;
//攻击力
BitConverter.GetBytes(atk).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(short);
//性别
BitConverter.GetBytes(sex).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(bool);
return playerBytes;
}
}
public class Lesson15_网络通信_通信必备知识_序列化和反序列化2进制数据_序列化 : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
#region 知识点一 非字符串类型转字节数组
//关键类:BitConverter
//所在命名空间:System
//主要作用:除字符串的其它常用类型和字节数组相互转换
byte[] byteArray1 = BitConverter.GetBytes(1);
#endregion
#region 知识点二 字符串类型转字节数组
//关键类:Encoding
//所在命名空间:System.Text
//主要作用:将字符串类型和字节数组相互转换,并且决定转换时使用的字符编码类型,网络通信时建议大家使用UTF-8类型
byte[] byteArray2 = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("人间自有韬哥在");
#endregion
#region 知识点三 如何将一个类对象转换为二进制
//注意:网络通信中我们不能直接使用数据持久化2进制知识点中的
//BinaryFormatter 2进制格式化类
//因为客户端和服务器使用的语言可能不一样,BinaryFormatter是C#的序列化规则,和其它语言之间的兼容性不好
//如果使用它,那么其它语言开发的服务器无法对其进行反序列化
//我们需要自己来处理将类对象数据序列化为字节数组
//单纯的转换一个变量为字节数组非常的简单
//但是我们如何将一个类对象携带的所有信息放入到一个字节数组中呢
//我们需要做以下几步
//1.明确 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组 的容量(注意:在确定字符串字节长度时要考虑解析时如何处理)
PlayerInfo playerInfo = new PlayerInfo();
playerInfo.lev = 10;
playerInfo.name = "韬老狮";
playerInfo.atk = 88;
playerInfo.sex = false;
//得到的 这个Info数据 如果转换成 字节数组 那么字节数组容器需要的容量
int indexNum = sizeof(int) + //lev int类型 4
sizeof(int) + //代表 name字符串转换成字节数组后 name数组的长度 4
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(playerInfo.name).Length + //name字符串具体字节数组的长度
sizeof(short) + //atk short类型 2
sizeof(bool); //sex bool类型 1
//2.申明一个 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器
byte[] playerBytes = new byte[indexNum];
//3.将对象中的所有信息转为字节数组并放入 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器 中(可以利用数组中的CopeTo方法转存字节数组)
//CopyTo方法的第二个参数代表 从容器的第几个位置开始存储
int index = 0;//从 playerBytes数组中的第几个位置去存储数据
//等级 把等级转成字节数组 拷贝到 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器
BitConverter.GetBytes(playerInfo.lev).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);//索引加上对应字节
//姓名 姓名长度是不固定的 所以要先存姓名长度 用int来存
byte[] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(playerInfo.name);
int num = strBytes.Length;//姓名占多少字节
//存储的是姓名转换成字节数组后 字节数组的长度
BitConverter.GetBytes(num).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);//索引加上对应字节
//存储字符串的字节数组 真正的存入姓名
strBytes.CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += num;//存入姓名后加上索引
//攻击力 把攻击力转成字节数组 拷贝到 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器
BitConverter.GetBytes(playerInfo.atk).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(short);//索引加上对应字节
//性别 把性别转成字节数组 拷贝到 装载playerInfo 所有数据信息 的字节数组容器
BitConverter.GetBytes(playerInfo.sex).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(bool);//索引加上对应字节
#endregion
#region 总结
//我们对类对象的2进制序列化主要用到的知识点是
//1.BitConverter转换非字符串的类型的变量为字节数组
//2.Encoding.UTF8转换字符串类型的变量为字节数组(注意:为了考虑反序列化,我们在转存2进制,序列化字符串之前,先序列化字符串字节数组的长度)
//转换流程是
//1.明确字节数组的容量
//2.申明一个装载信息的字节数组容器
//3.将对象中的所有信息转为字节数组并放入该容器当中(利用数组中的CopeTo方法转存字节数组)
#endregion
}
}
15.3 练习题
请写一个序列化基类,让我们可以更方便进行自定义类的序列化操作
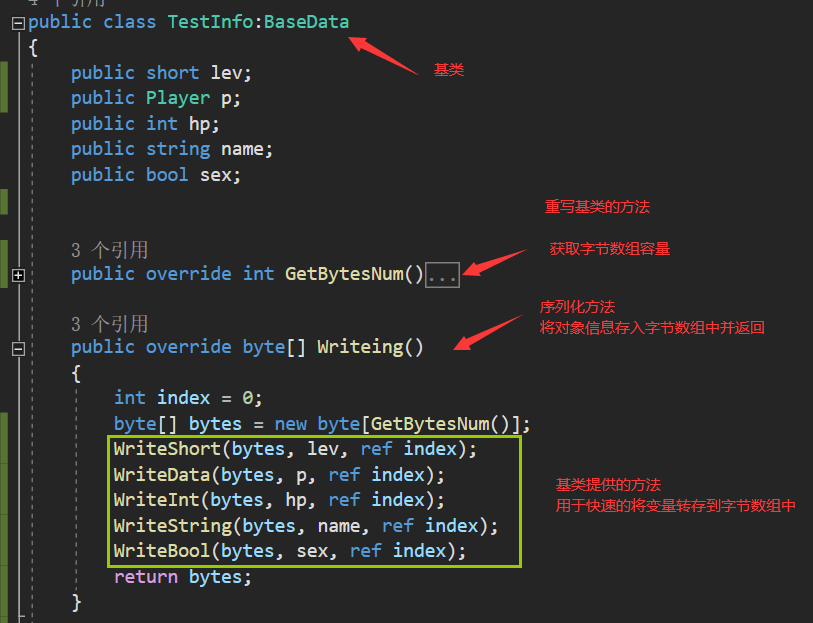
声明自定义序列化转换类
public abstract class BaseData
{
/// <summary>
/// 用于子类重写的 获取字节数组容器大小的方法
/// </summary>
/// <returns>对象需要占用的字节数</returns>
public abstract int GetBytesNum();
/// <summary>
/// 将对象的成员变量序列化为对应的字节数组
/// </summary>
/// <returns>序列化后的字节数组</returns>
public abstract byte[] Writing();
#region 存储
/// <summary>
/// 存储整型变量到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的整数值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteInt(byte[] bytes, int value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储短整型变量到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的短整数值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteShort(byte[] bytes, short value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(short);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储长整型变量到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的长整数值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteLong(byte[] bytes, long value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(long);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储单精度浮点数到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的单精度浮点数值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteFloat(byte[] bytes, float value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(float);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储字节到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的字节值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteByte(byte[] bytes, byte value, ref int index)
{
bytes[index] = value;
index += sizeof(byte);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储布尔值到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的布尔值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteBool(byte[] bytes, bool value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(bool);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储字符串到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的字符串值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteString(byte[] bytes, string value, ref int index)
{
// 先存储字符串字节数组的长度
byte[] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(value);
WriteInt(bytes, strBytes.Length, ref index);
// 再存储字符串字节数组
strBytes.CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += strBytes.Length;
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储自定义数据对象到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="data">具体的自定义数据对象</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteData(byte[] bytes, BaseData data, ref int index)
{
data.Writing().CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += data.GetBytesNum();
}
#endregion
}
两个测试类,存在嵌套
public class TestInfo : BaseData
{
public short lev; // 玩家等级
public Player player; // 玩家对象
public int hp; // 生命值
public string name; // 玩家名称
public bool sex; // 玩家性别
public override int GetBytesNum()
{
// 返回对象需要占用的字节数,按照各个成员的大小累加
return sizeof(short) + // 2 字节
player.GetBytesNum() + // 玩家对象序列化大小
sizeof(int) + // 4 字节
4 + Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(name).Length + // 字符串长度(4字节) + 字符串字节数
sizeof(bool); // 1 字节
}
public override byte[] Writing()
{
int index = 0; // 用于记录当前序列化位置的索引
byte[] bytes = new byte[GetBytesNum()]; // 创建字节数组
WriteShort(bytes, lev, ref index); // 序列化玩家等级
WriteData(bytes, player, ref index); // 序列化玩家对象
WriteInt(bytes, hp, ref index); // 序列化生命值
WriteString(bytes, name, ref index); // 序列化玩家名称
WriteBool(bytes, sex, ref index); // 序列化玩家性别
// 序列化列表的长度以及循环序列化对应的内容
return bytes; // 返回序列化后的字节数组
}
}
public class Player : BaseData
{
public int atk; // 玩家攻击力
public override int GetBytesNum()
{
return 4; // 返回对象需要占用的字节数,此处为 4 字节
}
public override byte[] Writing()
{
int index = 0; // 用于记录当前序列化位置的索引
byte[] bytes = new byte[GetBytesNum()]; // 创建字节数组
WriteInt(bytes, atk, ref index); // 序列化玩家攻击力
return bytes; // 返回序列化后的字节数组
}
}
得到对象的字节数组
// 创建 TestInfo 对象用于存储数据
TestInfo testInfo = new TestInfo();
// 设置 TestInfo 对象的各个成员变量的值
testInfo.lev = 87; // 设置玩家等级
testInfo.player = new Player(); // 创建 Player 对象并设置玩家对象
testInfo.player.atk = 77; // 设置玩家攻击力
testInfo.hp = 100; // 设置生命值
testInfo.name = "人间自有韬哥在"; // 设置玩家名称
testInfo.sex = false; // 设置玩家性别
// 调用 TestInfo 对象的 Writing 方法,将数据序列化为字节数组
byte[] testInfoByteArray = testInfo.Writing();
15.4 练习题代码
BaseData
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using UnityEngine;
public abstract class BaseData
{
/// <summary>
/// 用于子类重写的 获取字节数组容器大小的方法
/// </summary>
/// <returns>对象需要占用的字节数</returns>
public abstract int GetBytesNum();
/// <summary>
/// 将对象的成员变量序列化为对应的字节数组
/// </summary>
/// <returns>序列化后的字节数组</returns>
public abstract byte[] Writing();
/// <summary>
/// 将二进制字节数组反序列化到对象的成员变量中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">反序列化使用的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="beginIndex">从该字节数组的第几个位置开始解析,默认为0</param>
/// <returns>已解析的字节数</returns>
public abstract int Reading(byte[] bytes, int beginIndex = 0);
#region 存储
/// <summary>
/// 存储整型变量到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的整数值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteInt(byte[] bytes, int value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储短整型变量到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的短整数值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteShort(byte[] bytes, short value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(short);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储长整型变量到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的长整数值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteLong(byte[] bytes, long value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(long);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储单精度浮点数到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的单精度浮点数值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteFloat(byte[] bytes, float value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(float);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储字节到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的字节值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteByte(byte[] bytes, byte value, ref int index)
{
bytes[index] = value;
index += sizeof(byte);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储布尔值到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的布尔值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteBool(byte[] bytes, bool value, ref int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(bool);
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储字符串到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="value">具体的字符串值</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteString(byte[] bytes, string value, ref int index)
{
// 先存储字符串字节数组的长度
byte[] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(value);
WriteInt(bytes, strBytes.Length, ref index);
// 再存储字符串字节数组
strBytes.CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += strBytes.Length;
}
/// <summary>
/// 存储自定义数据对象到指定的字节数组中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">指定的字节数组</param>
/// <param name="data">具体的自定义数据对象</param>
/// <param name="index">每次存储后用于记录当前索引位置的变量</param>
protected void WriteData(byte[] bytes, BaseData data, ref int index)
{
data.Writing().CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += data.GetBytesNum();
}
#endregion
#region 读取
/// <summary>
/// 根据字节数组读取整数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">字节数组</param>
/// <param name="index">开始读取的索引数</param>
/// <returns>读取到的整数值</returns>
protected int ReadInt(byte[] bytes, ref int index)
{
int value = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
return value;
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据字节数组读取短整数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">字节数组</param>
/// <param name="index">开始读取的索引数</param>
/// <returns>读取到的短整数值</returns>
protected short ReadShort(byte[] bytes, ref int index)
{
short value = BitConverter.ToInt16(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(short);
return value;
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据字节数组读取长整数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">字节数组</param>
/// <param name="index">开始读取的索引数</param>
/// <returns>读取到的长整数值</returns>
protected long ReadLong(byte[] bytes, ref int index)
{
long value = BitConverter.ToInt64(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(long);
return value;
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据字节数组读取单精度浮点数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">字节数组</param>
/// <param name="index">开始读取的索引数</param>
/// <returns>读取到的单精度浮点数值</returns>
protected float ReadFloat(byte[] bytes, ref int index)
{
float value = BitConverter.ToSingle(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(float);
return value;
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据字节数组读取字节
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">字节数组</param>
/// <param name="index">开始读取的索引数</param>
/// <returns>读取到的字节值</returns>
protected byte ReadByte(byte[] bytes, ref int index)
{
byte value = bytes[index];
index += sizeof(byte);
return value;
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据字节数组读取布尔值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">字节数组</param>
/// <param name="index">开始读取的索引数</param>
/// <returns>读取到的布尔值</returns>
protected bool ReadBool(byte[] bytes, ref int index)
{
bool value = BitConverter.ToBoolean(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(bool);
return value;
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据字节数组读取字符串
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bytes">字节数组</param>
/// <param name="index">开始读取的索引数</param>
/// <returns>读取到的字符串值</returns>
protected string ReadString(byte[] bytes, ref int index)
{
// 首先读取长度
int length = ReadInt(bytes, ref index);
// 再读取字符串
string value = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes, index, length);
index += length;
return value;
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据字节数组读取自定义数据对象
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">自定义数据对象的类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="bytes">字节数组</param>
/// <param name="index">开始读取的索引数</param>
/// <returns>已读取的自定义数据对象</returns>
protected T ReadData<T>(byte[] bytes, ref int index) where T : BaseData, new()
{
T value = new T();
index += value.Reading(bytes, index);
return value;
}
#endregion
}
TestInfo
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using UnityEngine;
public class TestInfo : BaseData
{
public short lev; // 玩家等级
public Player player; // 玩家对象
public int hp; // 生命值
public string name; // 玩家名称
public bool sex; // 玩家性别
public override int GetBytesNum()
{
// 返回对象需要占用的字节数,按照各个成员的大小累加
return sizeof(short) + // 2 字节
player.GetBytesNum() + // 玩家对象序列化大小
sizeof(int) + // 4 字节
4 + Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(name).Length + // 字符串长度(4字节) + 字符串字节数
sizeof(bool); // 1 字节
}
public override byte[] Writing()
{
int index = 0; // 用于记录当前序列化位置的索引
byte[] bytes = new byte[GetBytesNum()]; // 创建字节数组
WriteShort(bytes, lev, ref index); // 序列化玩家等级
WriteData(bytes, player, ref index); // 序列化玩家对象
WriteInt(bytes, hp, ref index); // 序列化生命值
WriteString(bytes, name, ref index); // 序列化玩家名称
WriteBool(bytes, sex, ref index); // 序列化玩家性别
// 序列化列表的长度以及循环序列化对应的内容
return bytes; // 返回序列化后的字节数组
}
public override int Reading(byte[] bytes, int beginIndex = 0)
{
int index = beginIndex; // 用于记录当前反序列化位置的索引
lev = ReadShort(bytes, ref index); // 反序列化玩家等级
player = ReadData<Player>(bytes, ref index); // 反序列化玩家对象
hp = ReadInt(bytes, ref index); // 反序列化生命值
name = ReadString(bytes, ref index); // 反序列化玩家名称
sex = ReadBool(bytes, ref index); // 反序列化玩家性别
// 反序列化列表的长度以及循环反序列化对应的内容
return index - beginIndex; // 返回已反序列化的字节数
}
}
public class Player : BaseData
{
public int atk; // 玩家攻击力
public override int GetBytesNum()
{
return 4; // 返回对象需要占用的字节数,此处为 4 字节
}
public override byte[] Writing()
{
int index = 0; // 用于记录当前序列化位置的索引
byte[] bytes = new byte[GetBytesNum()]; // 创建字节数组
WriteInt(bytes, atk, ref index); // 序列化玩家攻击力
return bytes; // 返回序列化后的字节数组
}
public override int Reading(byte[] bytes, int beginIndex = 0)
{
int index = beginIndex; // 用于记录当前反序列化位置的索引
atk = ReadInt(bytes, ref index); // 反序列化玩家攻击力
return index - beginIndex; // 返回已反序列化的字节数
}
}
Lesson15_练习题
public class Lesson15_练习题 : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
// 创建 TestInfo 对象用于存储数据
TestInfo testInfo = new TestInfo();
// 设置 TestInfo 对象的各个成员变量的值
testInfo.lev = 87; // 设置玩家等级
testInfo.player = new Player(); // 创建 Player 对象并设置玩家对象
testInfo.player.atk = 77; // 设置玩家攻击力
testInfo.hp = 100; // 设置生命值
testInfo.name = "人间自有韬哥在"; // 设置玩家名称
testInfo.sex = false; // 设置玩家性别
// 调用 TestInfo 对象的 Writing 方法,将数据序列化为字节数组
byte[] testInfoByteArray = testInfo.Writing();
}
}
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 785293209@qq.com

