4.行为型模式-迭代器模式
4.1 基础知识
学习难度:3
使用频率:5
总分:8
定义
迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不暴露该对象的内部表示。
说人话
以统一的方式遍历不同类型的集合。
结构图
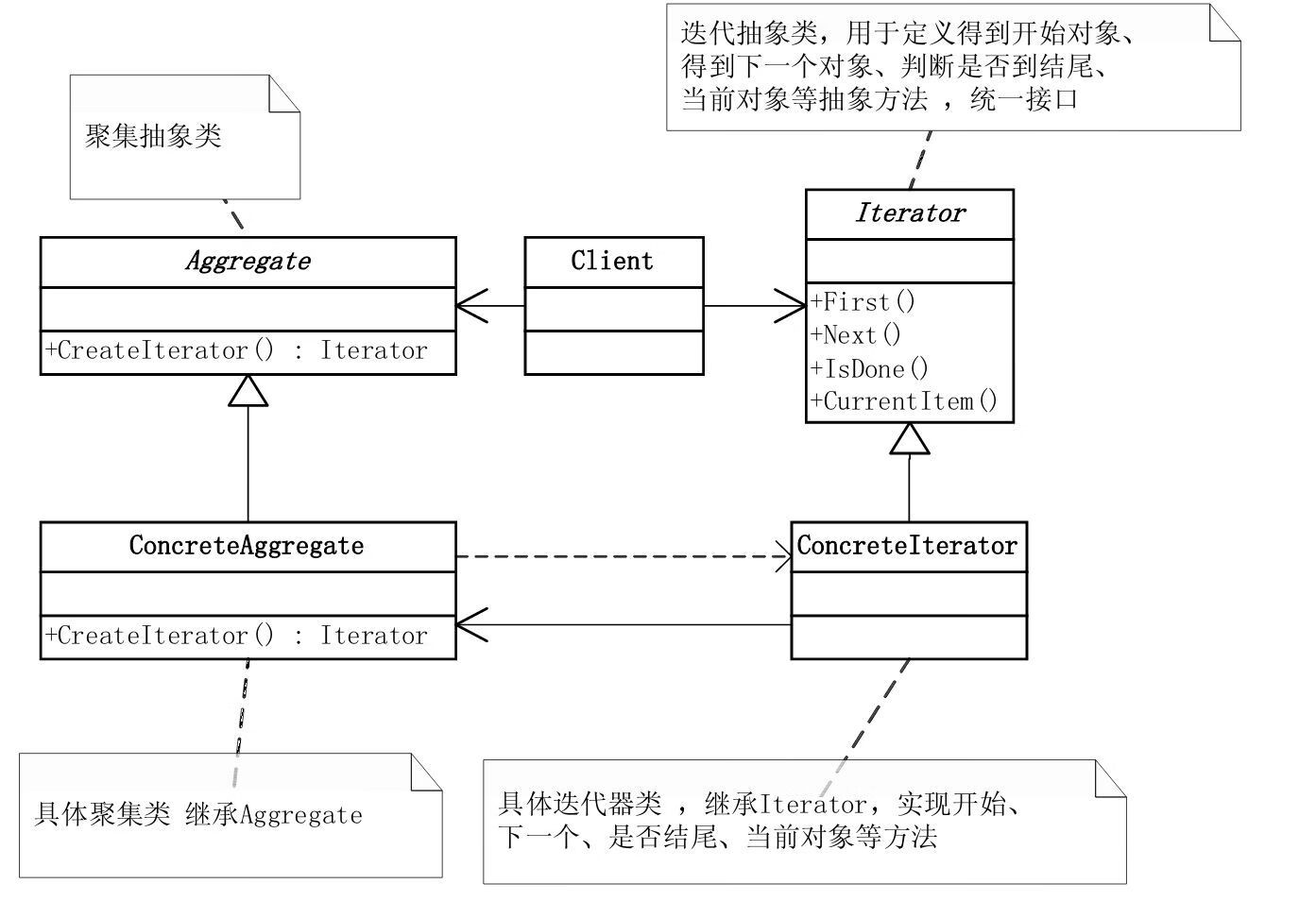
实现步骤
- 常规实现迭代器
- 迭代器接口
- 定义移动到下一元素方法并返回能否移动
- 定义获得当前元素属性
- 定义重置迭代器位置方法
- 集合接口
- 定义创建迭代器方法并返回迭代器接口方法
- 具体集合类
- 实现集合接口
- 定义集合并在构造函数中初始化集合
- 实现创建迭代器方法,方法中实例化一个新的具体迭代器并返回,传入自身作为参数
- 提供长度属性返回当前集合中的长度
- 提供索引器返回集合中元素
- 具体迭代器类
- 实现迭代器接口
- 定义具体集合类对象并在构造函数初始化传入
- 定义索引变量
- 实现移动到下一元素方法让索引+1并返回是否超出了具体集合类对象中的集合的长度
- 当前元素的属性中判断索引合法后返回具体集合类对象中的集合在当前索引下的对象
- 重置迭代器位置的方法中设置索引为-1
- 客户端
- 实例化具体集合
- 调用具体集合的创建迭代器方法得到具体迭代器
- 使用 While 循环判断条件中调用具体迭代器的移动到下一元素方法判断是否有下一元素
- 循环中得到具体迭代器的当前元素的属性进行操作
- 跳出循环后可以重置迭代器位置
- 迭代器接口
- .Net 实现迭代器
- 迭代器接口:已被定义
- 集合接口:已被定义
- 具体集合类:可以和常规实现,也可以在实现创建迭代器方法中遍历集合,每次循环使用 yield return 语法糖返回当前元素,编译器会自动生成具体迭代器
- 具体迭代器类:可以和常规实现相同。如果具体集合类使用了 yield return 语法糖,可以不实现具体迭代器类
- 使用时:实例化具体集合,直接使用 foreach 进行遍历
说明
迭代器模式已集成到 .Net 了,大部分情况不需要自己写。
4.2 模版代码
迭代器接口和具体迭代器类
// 迭代器接口
public interface IIterator
{
bool MoveNext(); // 移动到下一元素并返回是否移动成功
object Current { get; } // 获得当前元素属性
void Reset(); // 重置迭代器位置
}
// 具体迭代器类
public class ConcreteIterator : IIterator
{
private ConcreteCollection collection;
private int index = -1;
public ConcreteIterator(ConcreteCollection collection)
{
this.collection = collection;
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
index++;
return index < collection.Count; // 返回是否成功移动到下一元素
}
public object Current => collection[index];
public void Reset()
{
index = -1; // 重置迭代器位置
}
}
集合接口和具体集合类
// 集合接口
public interface ICollection
{
IIterator GetIterator(); // 创建迭代器
}
// 具体集合类
public class ConcreteCollection : ICollection
{
private List<object> items = new List<object>();
public ConcreteCollection()
{
// 在构造函数中初始化集合
items.Add("元素1");
items.Add("元素2");
items.Add("元素3");
}
public IIterator GetIterator()
{
// 实例化一个新的具体迭代器并返回,将集合传递给迭代器
return new ConcreteIterator(this);
}
// 集合长度
public int Count
{
get { return items.Count; }
}
// 添加索引器
public object this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index >= 0 && index < items.Count)
{
return items[index];
}
else
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("Index is out of range.");
}
}
set
{
if (index >= 0 && index < items.Count)
{
items[index] = value;
}
else
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("Index is out of range.");
}
}
}
}
客户端
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ConcreteCollection collection = new ConcreteCollection();
IIterator iterator = collection.GetIterator();
while (iterator.MoveNext())
{
object item = iterator.Current;
Console.WriteLine("当前元素:" + item);
// 当前元素:元素1
// 当前元素:元素2
// 当前元素:元素3
}
iterator.Reset(); // 重置迭代器位置
while (iterator.MoveNext())
{
object item = iterator.Current;
Console.WriteLine("第二遍遍历:" + item);
// 第二遍遍历:元素1
// 第二遍遍历:元素2
// 第二遍遍历:元素3
}
}
}
4.3 CSharp实践
实践需求
使用.Net定义好的迭代器接口和语法糖,实现迭代器遍历
具体迭代器类
// 具体迭代器类 其实是不需要具体迭代器类 在具体集合类使用yield return 语法糖
public class ConcreteEnumerator : IEnumerator
{
private ConcreteEnumerable enumerable;
private int index = -1;
public ConcreteEnumerator(ConcreteEnumerable enumerable)
{
this.enumerable = enumerable;
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
index++;
return index < enumerable.Count; // 返回是否成功移动到下一元素
}
public object Current => enumerable[index];
public void Reset()
{
index = -1; // 重置迭代器位置
}
}
具体集合类
// 具体集合类
public class ConcreteEnumerable : IEnumerable
{
private List<object> items = new List<object>();
public ConcreteEnumerable()
{
// 在构造函数中初始化集合
items.Add("元素1");
items.Add("元素2");
items.Add("元素3");
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
// 实例化一个新的具体迭代器并返回,将集合传递给迭代器
// 使用yield return语法糖更优雅
// return new ConcreteEnumerator(this);
for (int i = 0; i < items.Count; i++)
{
//yield关键字 配合迭代器使用
//可以理解为 暂时返回 保留当前的状态
//一会还会在回来
//C#的语法糖
//本质上其实还是有 Current属性 MoveNext方法 Reset方法
//只是系统检测到yield return关键字 帮我们做好了这部分逻辑
yield return items[i];
}
}
// 集合长度
public int Count
{
get { return items.Count; }
}
// 添加索引器
public object this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index >= 0 && index < items.Count)
{
return items[index];
}
else
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("Index is out of range.");
}
}
set
{
if (index >= 0 && index < items.Count)
{
items[index] = value;
}
else
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("Index is out of range.");
}
}
}
}
客户端
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ConcreteEnumerable enumerable = new ConcreteEnumerable();
// 常规使用具体迭代器遍历
// IEnumerator enumerator = enumerable.GetEnumerator();
// while (enumerator.MoveNext())
// {
// object item = enumerator.Current;
// Console.WriteLine("当前元素:" + item);
// // 当前元素:元素1
// // 当前元素:元素2
// // 当前元素:元素3
// }
//
// enumerator.Reset(); // 重置迭代器位置
//
// while (enumerator.MoveNext())
// {
// object item = enumerator.Current;
// Console.WriteLine("第二遍遍历:" + item);
// // 第二遍遍历:元素1
// // 第二遍遍历:元素2
// // 第二遍遍历:元素3
// }
//使用yield return语法糖后 使用foreach语法糖遍历 更优雅
foreach (var item in enumerable)
{
Console.WriteLine("当前元素:" + item);
// 当前元素:元素1
// 当前元素:元素2
// 当前元素:元素3
}
foreach (var item in enumerable)
{
Console.WriteLine("第二遍遍历:" + item);
// 第二遍遍历:元素1
// 第二遍遍历:元素2
// 第二遍遍历:元素3
}
}
}
4.4 Unity实践
实践需求
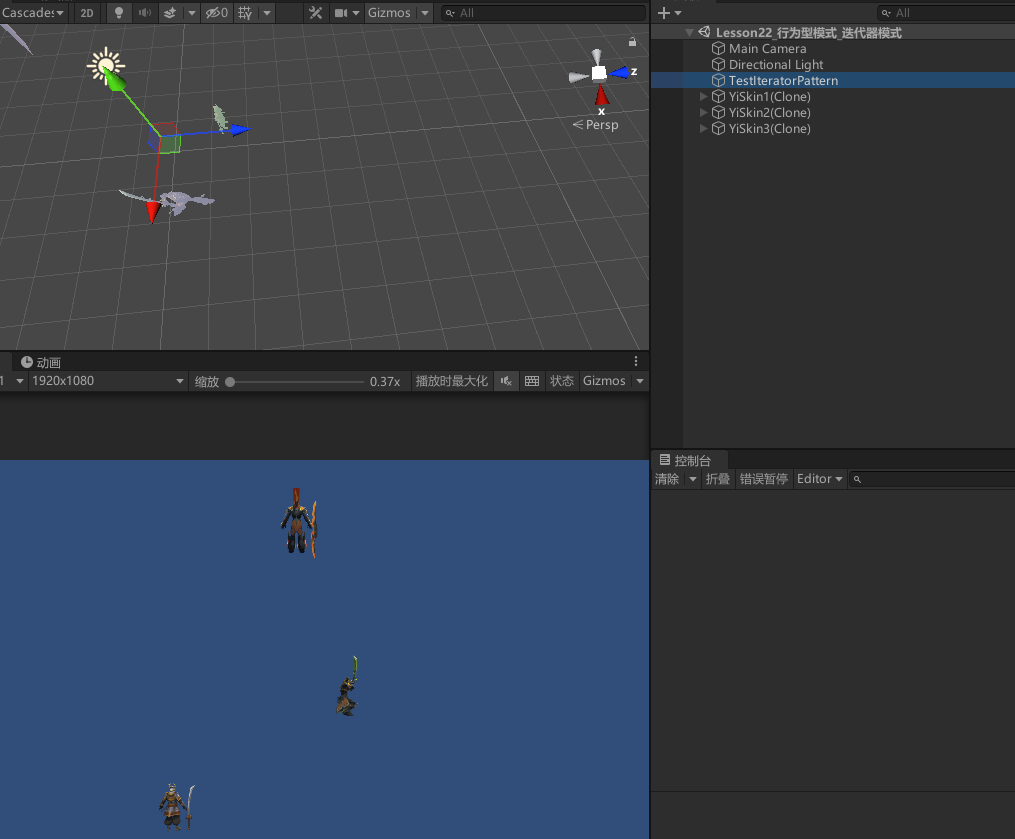
使用迭代器模式,遍历生成剑圣皮肤列表中的皮肤。
剑圣皮肤迭代器
public class ConcreteYiSkinList : IEnumerable
{
private readonly List<GameObject> yiSKinList;
public ConcreteYiSkinList()
{
GameObject yiSkin1 = Resources.Load<GameObject>("Lesson22_行为型模式_迭代器模式/YiSkin1");
GameObject yiSkin2 = Resources.Load<GameObject>("Lesson22_行为型模式_迭代器模式/YiSkin2");
GameObject yiSkin3 = Resources.Load<GameObject>("Lesson22_行为型模式_迭代器模式/YiSkin3");
yiSKinList = new List<GameObject>();
yiSKinList.Add(yiSkin1);
yiSKinList.Add(yiSkin2);
yiSKinList.Add(yiSkin3);
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
foreach (var t in yiSKinList)
{
yield return t;
}
}
}
客户端
public class TestIteratorPattern : MonoBehaviour
{
private void Start()
{
ConcreteYiSkinList yiSkinList = new ConcreteYiSkinList();
foreach (GameObject yiSkin in yiSkinList)
{
GameObject yiSkinGameObject = GameObject.Instantiate(yiSkin);
yiSkinGameObject.transform.position =
new Vector3(Random.Range(-5f, 5f), Random.Range(-5f, 5f), Random.Range(-5f, 5f));
}
}
}
运行结果
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 785293209@qq.com

