13.表面着色器-实例分析-法线贴图
13.1 知识点
在表面着色器中使用法线贴图
主要步骤
- 新建表面着色器
- 删除无关代码
- 声明相关属性
- 检查编译指令
- 编写相关逻辑
创建表面着色器,删除无关代码
Shader "Custom/Lesson13"
{
Properties
{
_Color ("Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_MainTex ("Albedo (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}
}
SubShader
{
Tags
{
"RenderType"="Opaque"
}
CGPROGRAM
// Physically based Standard lighting model, and enable shadows on all light types
#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows
// Use shader model 3.0 target, to get nicer looking lighting
#pragma target 3.0
sampler2D _MainTex;
struct Input
{
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
fixed4 _Color;
void surf(Input IN, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o)
{
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Diffuse"
}
声明法线贴图属性,并进行映射
// 定义材质属性,在 Inspector 面板中显示
Properties
{
//...
_BumpMap("BumpMap", 2D) = ""{} // 法线贴图
}
sampler2D _BumpMap;
检查编译指令
#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows // 使用标准光照模型和全前向阴影
#pragma target 3.0 // 指定 Shader 模型 3.0
在输入结构体中添加反映纹理 UV:
// 输入结构体:包含顶点传来的 UV 坐标
struct Input
{
float2 uv_MainTex;
float2 uv_BumpMap;
};
编写表面函数,设置基础颜色、漫反射颜色、透明度及切线空间下的法线
// 表面函数:计算最终材质效果
void surf(Input IN, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o)
{
// 从主纹理采样基础颜色
fixed4 texColor = tex2D(_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex);
// 漫反射颜色(纹理颜色 × 基础颜色)
o.Albedo = texColor.rgb * _Color.rgb;
// 透明度计算(纹理颜色 × 基础颜色)
o.Alpha = texColor.a * _Color.a;
// 从法线贴图解包法线,得到切线空间下的法线
o.Normal = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, IN.uv_BumpMap));
}
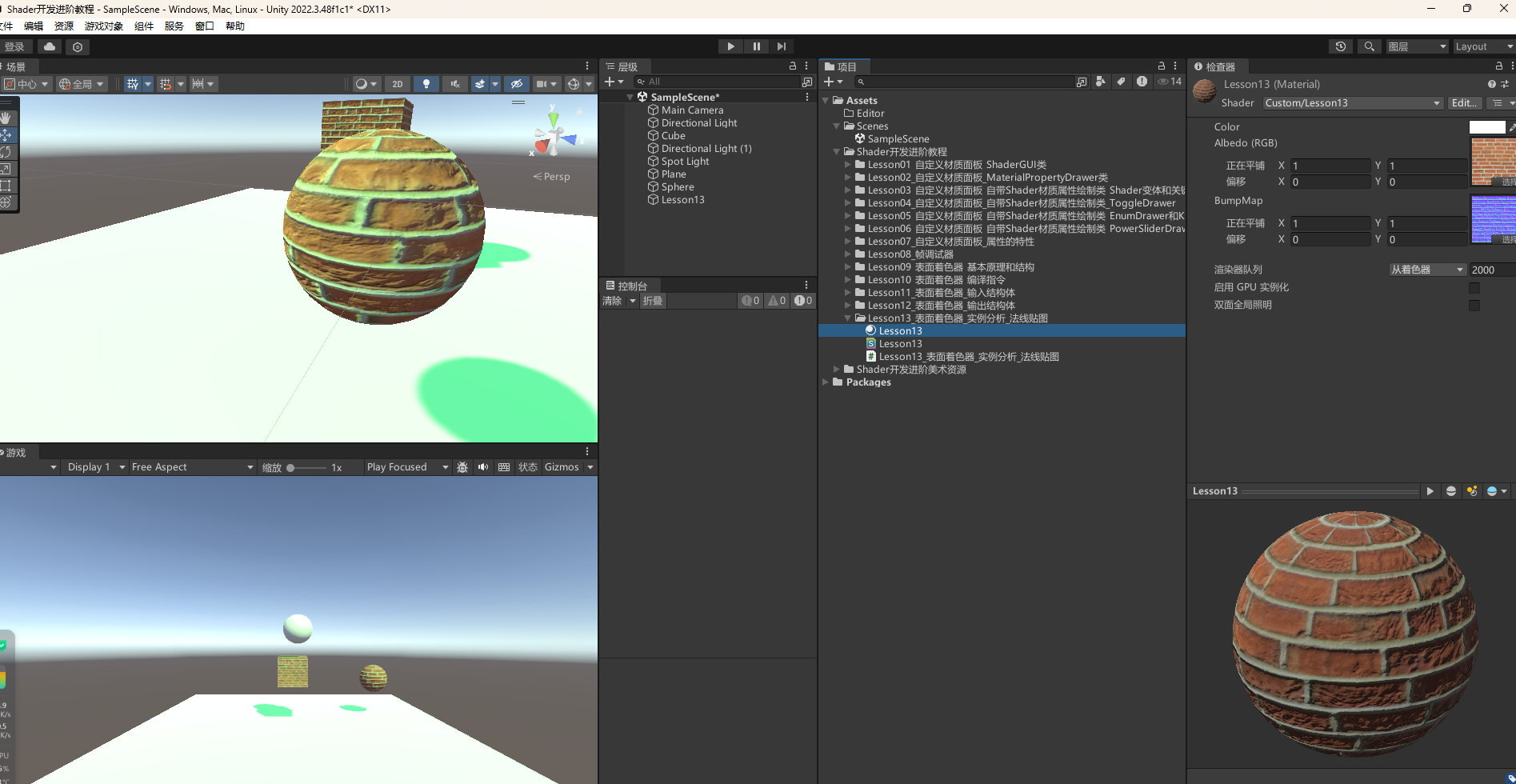
可以看到效果
输出结构体相关参数的使用
我们可以用 SurfaceOutputStandard 的发光程度、金属度和平滑度来举例。
设置发光属性并添加映射
Properties
{
_Color ("Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1) // 基础颜色
_MainTex ("Albedo (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {} // 颜色纹理
_BumpMap("BumpMap", 2D) = "{}" // 法线贴图
_Emission("Emission", Color) = (1,1,1,1) // 发光
_Metallic("Metallic", Range(0,1)) = 0 // 金属度
_Smoothness("Smoothness", Range(0,1)) = 0 // 平滑度
}
fixed4 _Emission;
fixed _Metallic;
fixed _Smoothness;
修改表面函数,设置发光效果、金属度和平滑度
// 表面函数:计算最终材质效果
void surf(Input IN, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o)
{
// 从主纹理采样基础颜色
fixed4 texColor = tex2D(_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex);
// 漫反射颜色(纹理颜色 × 基础颜色)
o.Albedo = texColor.rgb * _Color.rgb;
// 透明度计算(纹理颜色 × 基础颜色)
o.Alpha = texColor.a * _Color.a;
// 从法线贴图解包法线,得到切线空间下的法线
o.Normal = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, IN.uv_BumpMap));
// 设置发光效果、金属度和平滑度
o.Emission = _Emission.rgb;
o.Metallic = _Metallic;
o.Smoothness = _Smoothness;
}
查看效果
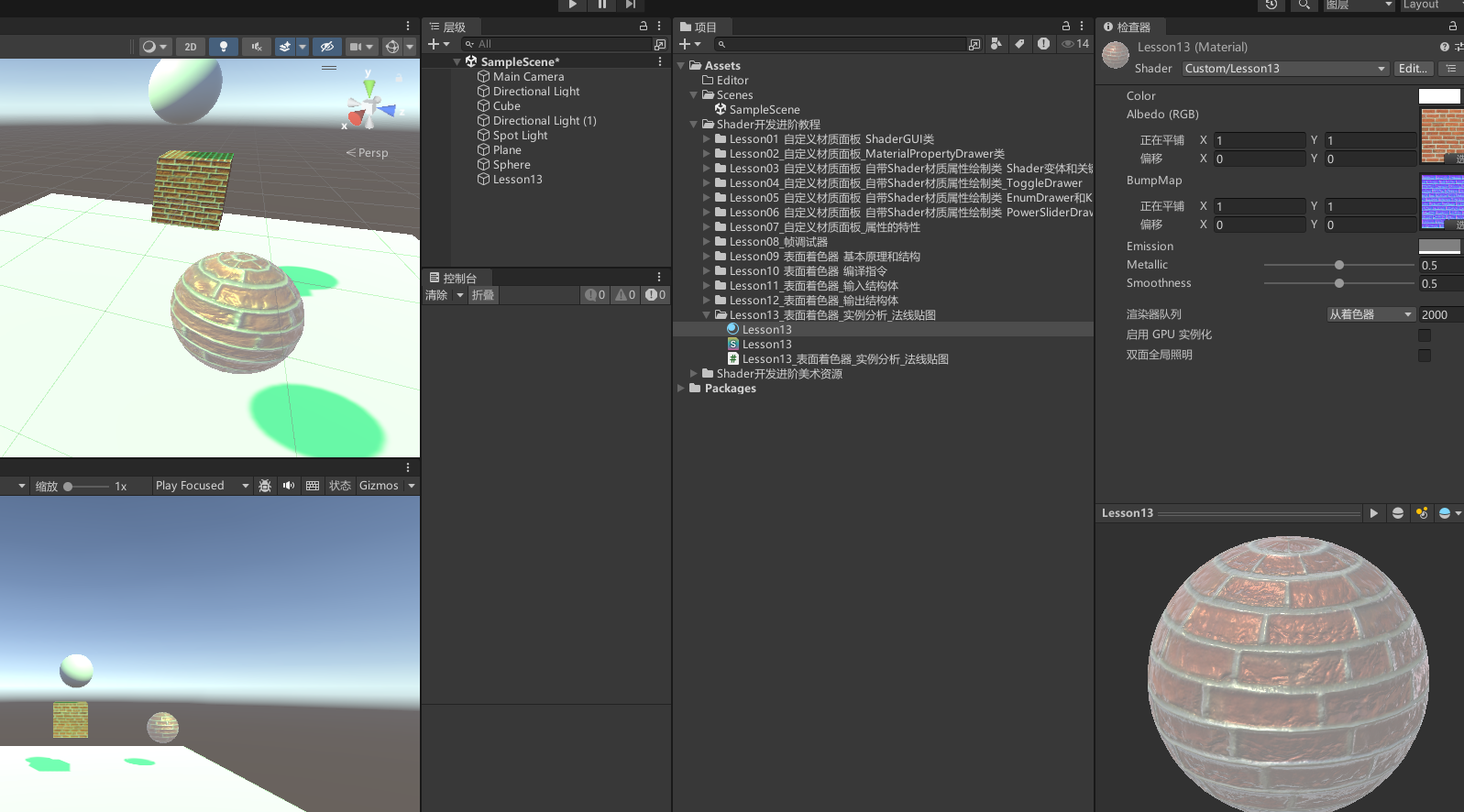
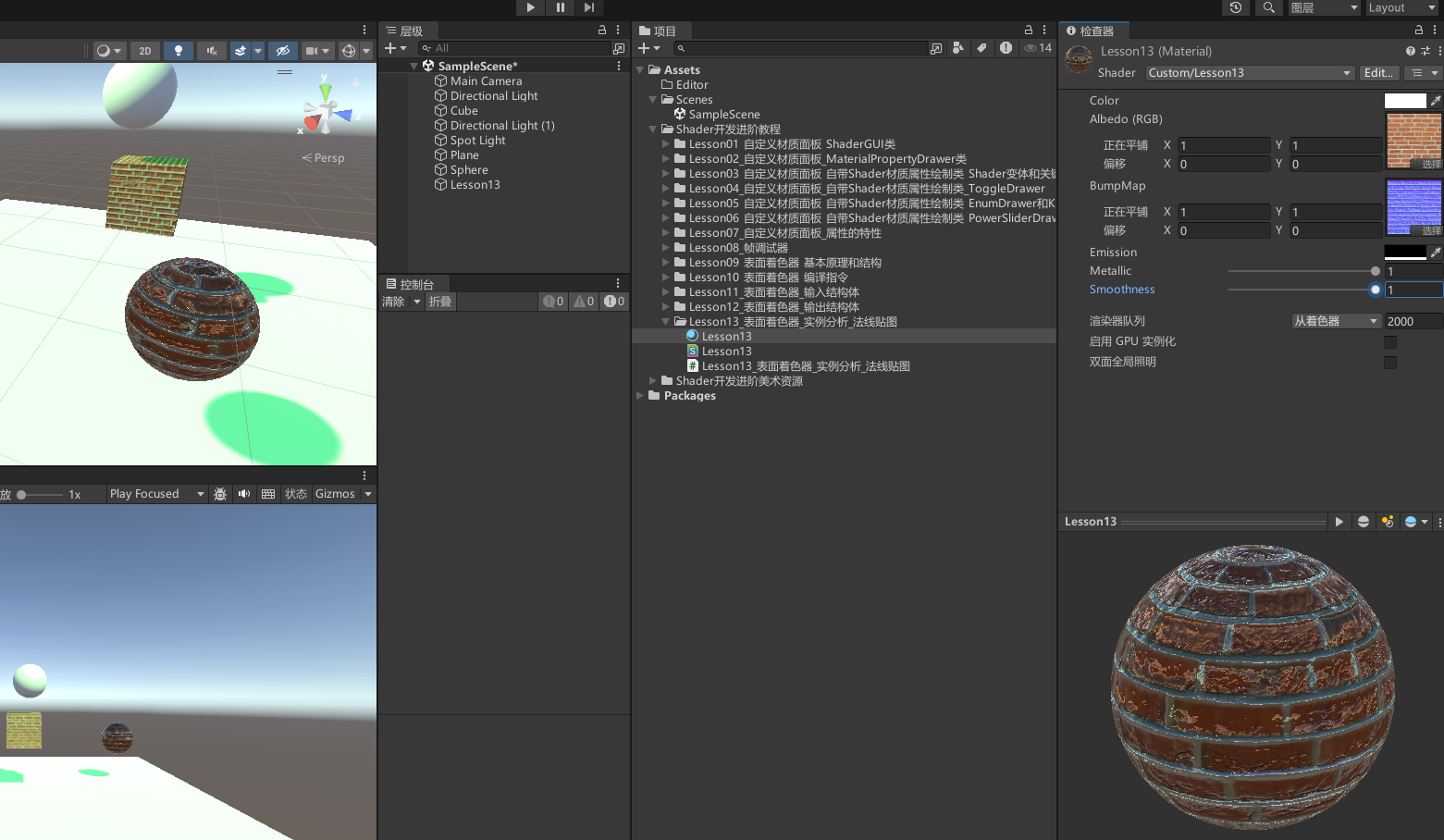
13.2 知识点代码
Lesson13.shader
Shader "Custom/Lesson13"
{
// 定义材质属性,在Inspector面板中显示
Properties
{
_Color ("Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1) // 基础颜色
_MainTex ("Albedo (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {} // 颜色纹理
_BumpMap("BumpMap", 2D) = ""{} // 法线贴图
_Emission("Emission", Color) = (1,1,1,1) // 发光
_Metallic("Metallic", Range(0,1)) = 0 // 金属度
_Smoothness("Smoothness", Range(0,1)) = 0 // 平滑度
}
SubShader
{
Tags
{
"RenderType"="Opaque"
} // 设置为不透明材质
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf Standard fullforwardshadows // 使用标准光照模型和全前向阴影
#pragma target 3.0 // 指定Shader模型3.0
// 声明属性变量
fixed4 _Color;
sampler2D _MainTex;
sampler2D _BumpMap;
fixed4 _Emission;
fixed _Metallic;
fixed _Smoothness;
// 输入结构体:包含顶点传来的UV坐标
struct Input
{
float2 uv_MainTex;
float2 uv_BumpMap;
};
// 表面函数:计算最终材质效果
void surf(Input IN, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o)
{
// 从主纹理采样基础颜色
fixed4 texColor = tex2D(_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex);
// 漫反射颜色(纹理颜色×基础颜色)
o.Albedo = texColor.rgb * _Color.rgb;
// 透明度计算 (纹理颜色×基础颜色)
o.Alpha = texColor.a * _Color.a;
// 从法线贴图解包法线 得到切线空间下的法线
o.Normal = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, IN.uv_BumpMap));
// 设置 发光效果 金属度和平滑度
o.Emission = _Emission.rgb;
o.Metallic = _Metallic;
o.Smoothness = _Smoothness;
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Diffuse" // 当该Shader无法使用时采用Diffuse Shader
}
Lesson13_表面着色器_实例分析_法线贴图.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Lesson13_表面着色器_实例分析_法线贴图 : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
#region 知识点一 在表面着色器中使用法线贴图
//1.新建表面着色器
//2.删除无关代码
//3.声明相关属性
//4.检查编译指令
//5.编写相关逻辑
#endregion
#region 知识点二 输出结构体相关参数的使用
//我们可以用SurfaceOutputStandard来举例
#endregion
}
}
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 785293209@qq.com

