19.面向对象-继承-多重继承
19.1 知识点
什么是多重继承
- 一个子类可以同时继承多个父类的机制。
基本语法
- 子类可以使用如下语法继承多个父类:
class 子类名 : 继承方式 父类名1, 继承方式 父类名2, ...
{
// 类体
};
- 示例使用:
Son s;
cout << s.bravery << endl;
cout << s.kindness << endl;
cout << s.speed << endl;
s.Sing();
s.Speech();
s.Run();
// 输出:
// 100
// 100
// 200
// 唱歌
// 演讲
// 跑步
同名成员问题
如果多个父类中存在同名成员,子类中需要通过
父类名::成员的方式明确作用域。示例代码:
cout << s.money << endl;
cout << s.Father::money << endl;
cout << s.Mother::money << endl;
s.Eat();
s.Father::Eat();
s.Mother::Eat();
// 输出:
// 0
// 5
// 100
// 儿子吃东西
// 爸爸吃东西
// 妈妈吃东西
构造与析构函数的调用顺序
构造函数调用顺序如下:
- 父类 → 子类成员对象 → 子类自身
- 多个父类之间按照继承顺序调用构造函数
析构函数调用顺序与构造顺序相反:
- 子类自身 → 子类成员对象 → 父类

19.2 知识点代码
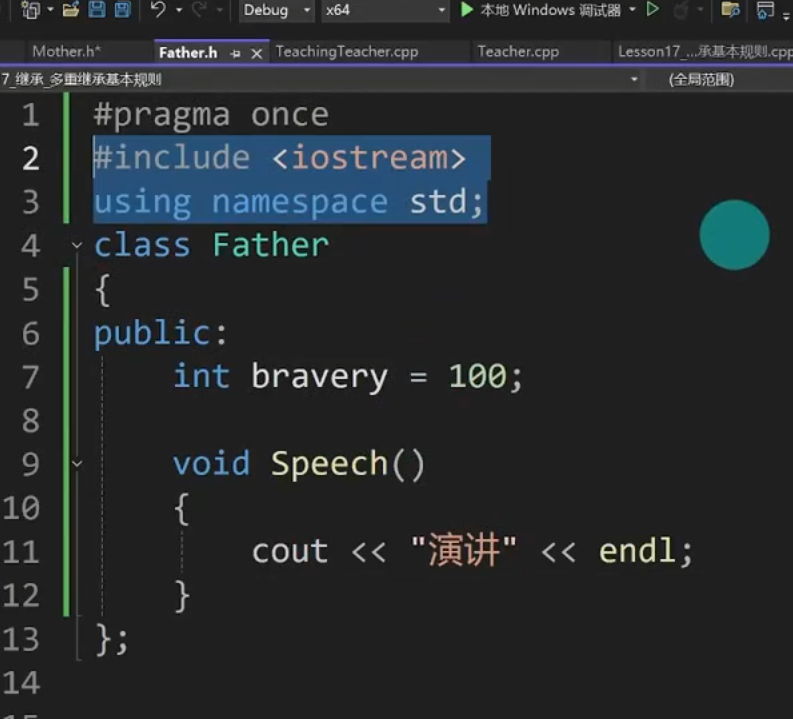
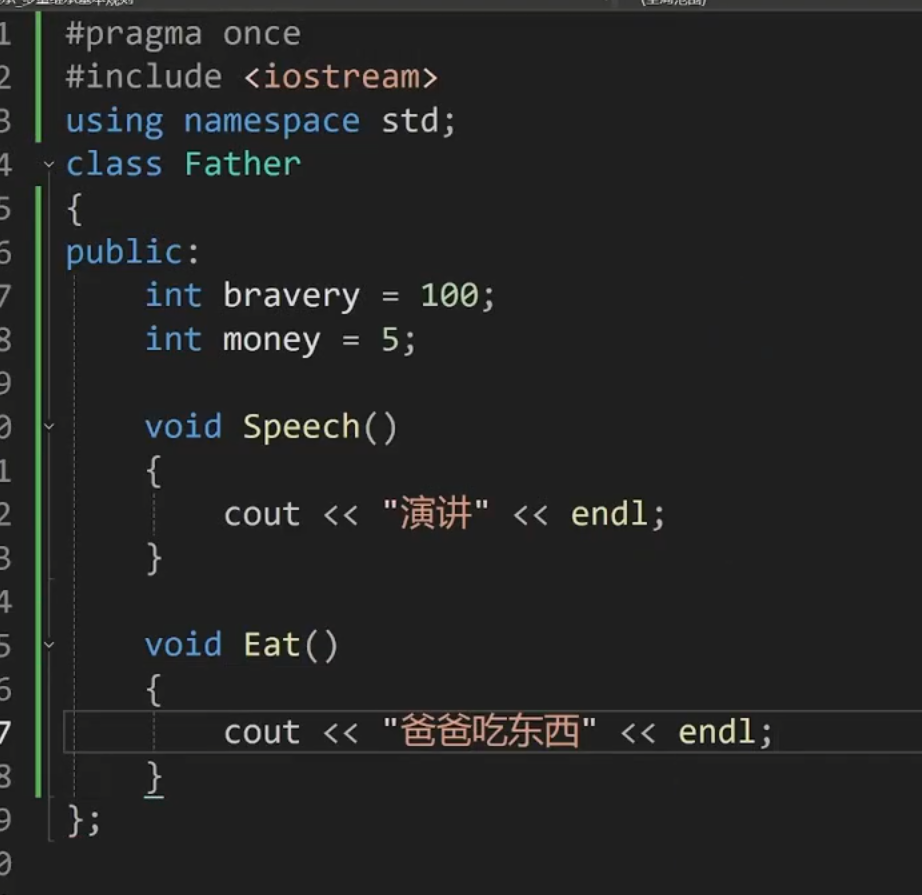
Father.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Father
{
public:
int bravery = 100;
int money = 5;
Father()
{
cout << "Father" << endl;
}
~Father()
{
cout << "~Father" << endl;
}
void Speech()
{
cout << "演讲" << endl;
}
void Eat()
{
cout << "爸爸吃东西" << endl;
}
};
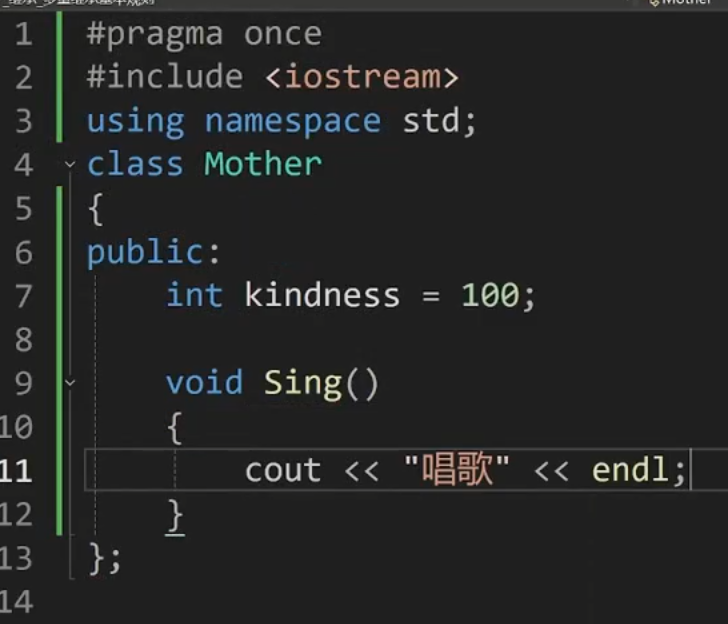
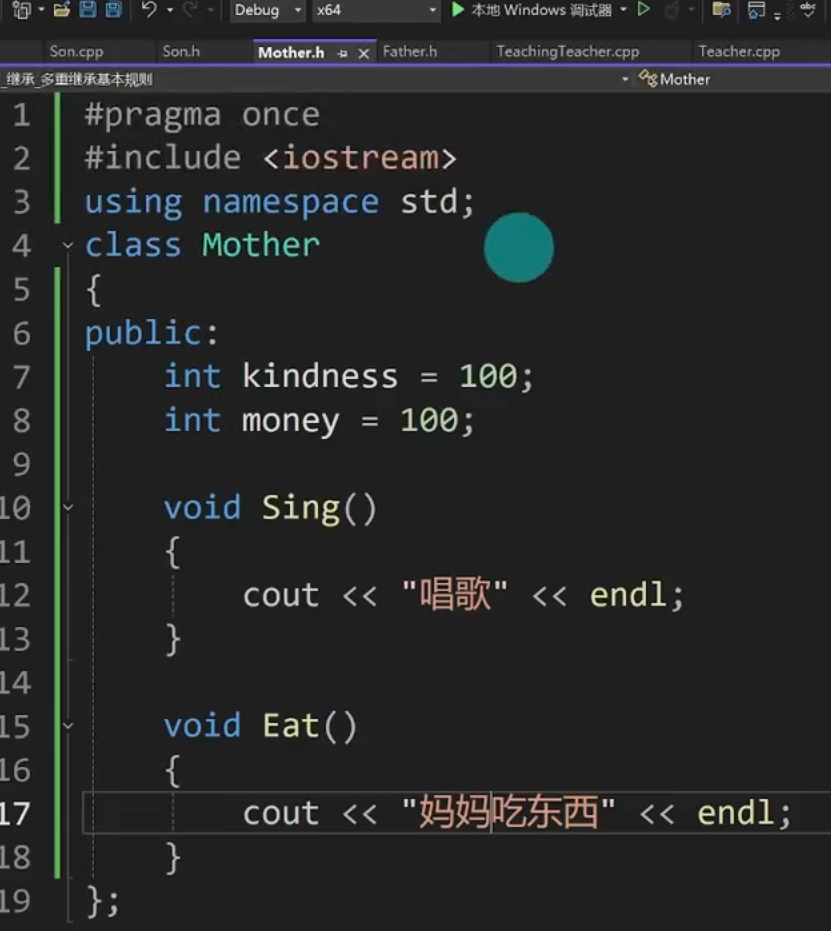
Mother.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Mother
{
public:
int kindness = 100;
int money = 100;
Mother()
{
cout << "Mother" << endl;
}
~Mother()
{
cout << "~Mother" << endl;
}
void Sing()
{
cout << "唱歌" << endl;
}
void Eat()
{
cout << "妈妈吃东西" << endl;
}
};
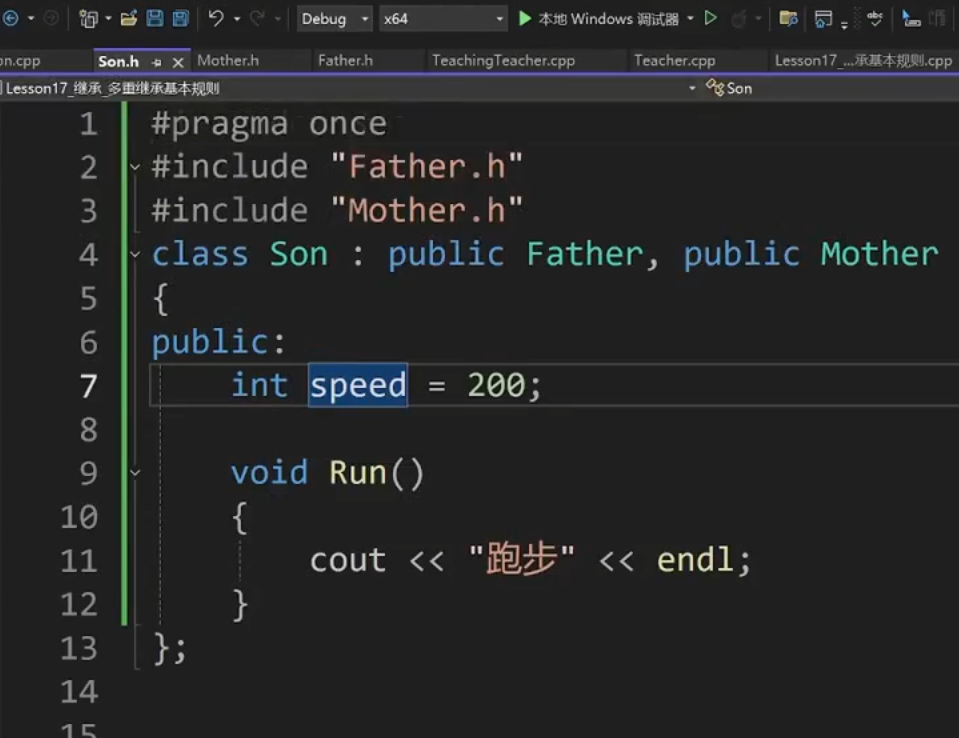
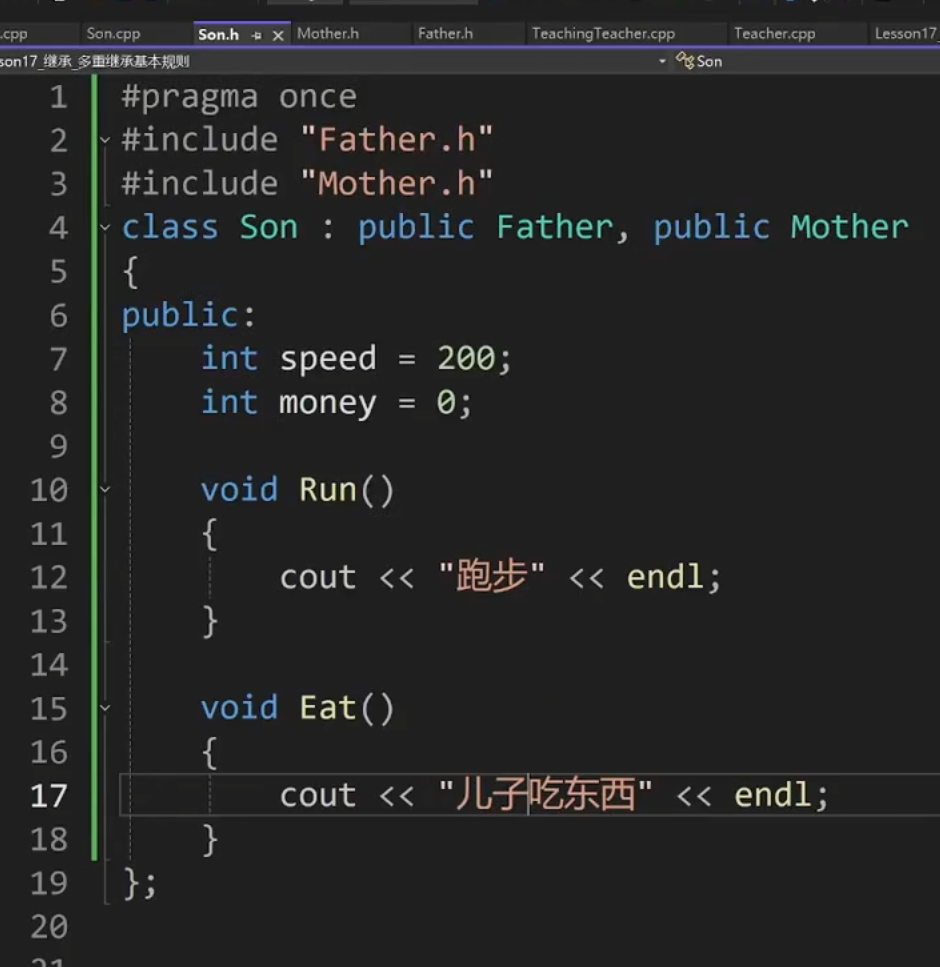
Son.h
#pragma once
#include "Father.h"
#include "Mother.h"
class Son : public Father, public Mother
{
public:
int speed = 200;
int money = 0;
Son()
{
cout << "Son" << endl;
}
~Son()
{
cout << "~Son" << endl;
}
void Run()
{
cout << "跑步" << endl;
}
void Eat()
{
//cout << Father::money << endl;
//Father::Eat();
cout << "儿子吃东西" << endl;
}
};
Lesson19_面向对象_继承_多重继承.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Son.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
#pragma region 知识点一 什么是多重继承
//一个子类可以同时继承多个父类的机制
#pragma endregion
#pragma region 知识点二 基本语法
//class 子类名: 继承方式 父类名1, 继承方式 父类名2, ....
//{
//}
Son s;
cout << s.bravery << endl;
cout << s.kindness << endl;
cout << s.speed << endl;
s.Sing();
s.Speech();
s.Run();
//100
//100
//200
//唱歌
//演讲
//跑步
#pragma endregion
#pragma region 知识点三 同名成员问题
//如果多个父类中存在同名成员,子类中需要
//通过 父类名::成员 的方式 明确作用域
cout << s.money << endl;
cout << s.Father::money << endl;
cout << s.Mother::money << endl;
s.Eat();
s.Father::Eat();
s.Mother::Eat();
//0
//5
//100
//儿子吃东西
//爸爸吃东西
//妈妈吃东西
#pragma endregion
#pragma region 知识点四 构造与析构函数的调用顺序
//构造顺序:
//父-子内-子,父之间按照继承顺序调用
//析构函数
//与构造顺序相反
#pragma endregion
}
19.3 练习题
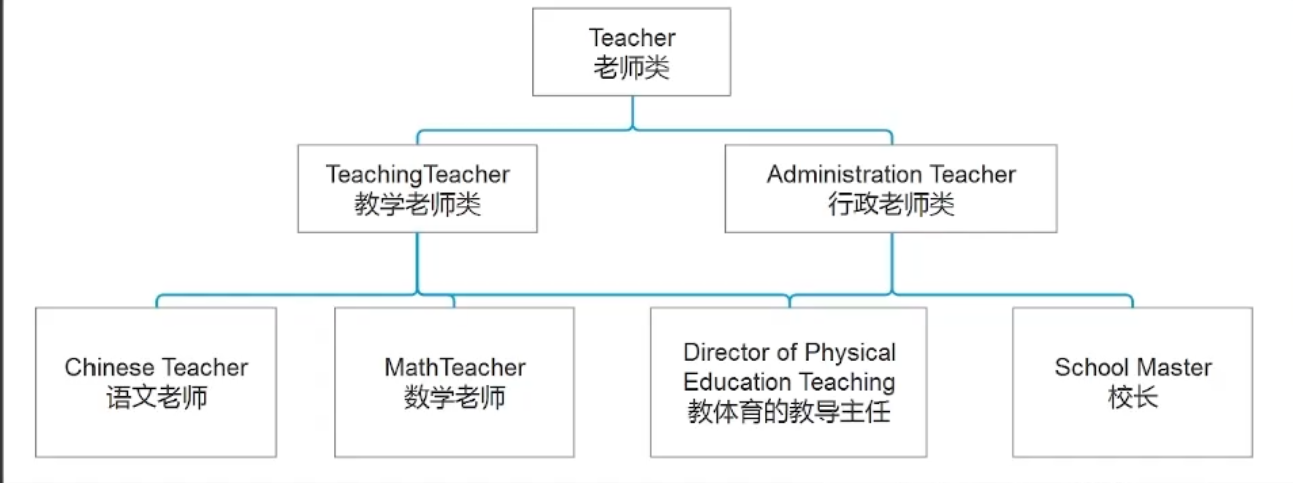
基于之前课程中实现的类(Teacher、TeachingTeacher),再实现两个类
请基于之前课程中实现的类(Teacher、TeachingTeacher),再实现两个类
1.行政老师类(有职位、行政特权特征,有行政特权执行行为)
2.教体育的教导主任(有跑步行为)
Teacher 类
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
public:
// 老师的名字
string name;
// 老师自我介绍的方法
void SpeakName()
{
number = 1;
f = 1.1f;
cout << name << endl;
}
protected:
int number;
private:
float f;
};
TeachingTeacher 类
#pragma once
#include "Teacher.h"
class TeachingTeacher : public Teacher
{
public:
string subject;
void SpeakSubject()
{
SpeakName();
// public 外部、内部、子类都能用
cout << name << endl; //(子类中使用)
// protected 内部、子类可以使用
cout << number << endl; //(子类中使用)
// private 内部使用
// cout << f << endl; //(子类中使用) — 不可访问
cout << subject << endl;
}
int x = 1;
void test()
{
cout << "TeachingTeacher" << endl;
}
};
AdministrationTeacher 类
#pragma once
#include "Teacher.h"
class AdministrationTeacher : public Teacher
{
public:
string job; // 职位
string administration; // 行政特权
void Execute()
{
cout << job << "执行" << administration << endl;
}
};
DOPET 类(多重继承:TeachingTeacher + AdministrationTeacher)
#pragma once
#include "TeachingTeacher.h"
#include "AdministrationTeacher.h"
class DOPET : public TeachingTeacher, public AdministrationTeacher
{
public:
void Run()
{
cout << "跑步" << endl;
}
};
使用示例
DOPET p;
p.TeachingTeacher::name = "小韬";
cout << p.TeachingTeacher::name << endl;
p.AdministrationTeacher::name = "小妍";
cout << p.AdministrationTeacher::name << endl;
p.TeachingTeacher::SpeakName();
p.AdministrationTeacher::SpeakName();
p.subject = "体育";
p.SpeakSubject();
p.job = "教导主任";
p.administration = "惩罚学生";
p.Execute();
p.Run();
// 小韬
// 小妍
// 小韬
// 小妍
// 小韬
// 小韬
// 1
// 体育
// 教导主任执行惩罚学生
// 跑步
19.4 练习题代码
Teacher.cs
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
public:
//老师的名字
string name;
//老师自我介绍的方法
void SpeakName()
{
number = 1;
f = 1.1f;
cout << name << endl;
}
protected:
int number;
private:
float f;
};
TeachingTeacher.cs
#pragma once
#include "Teacher.h"
class TeachingTeacher : public Teacher
{
public:
string subject;
void SpeakSubject()
{
SpeakName();
//public 外部 内部 子类都能用
cout << name << endl;//(子类中使用)
//protected 内部 子类可以使用
cout << number << endl;//(子类中使用)
//private 内部使用
//cout << f << endl;//(子类中使用)
cout << subject << endl;
}
int x = 1;
void test()
{
cout << "TeachingTeacher" << endl;
}
};
AdministrationTeacher.cs
#pragma once
#include "Teacher.h"
class AdministrationTeacher : public Teacher
{
public:
string job;//职位
string administration;//行政特权
void Execute()
{
cout << job << "执行" << administration << endl;
}
};
DOPET.cs
#pragma once
#include "TeachingTeacher.h"
#include "AdministrationTeacher.h"
class DOPET : public TeachingTeacher, public AdministrationTeacher
{
public:
void Run()
{
cout << "跑步" << endl;
}
};
Lesson19_练习题.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "DOPET.h"
int main()
{
#pragma region 练习题
/*请基于之前课程中实现的类(Teacher、TeachingTeacher),再实现两个类
1.行政老师类(有职位、行政特权特征,有行政特权执行行为)
2.教体育的教导主任(有跑步行为)*/
DOPET p;
p.TeachingTeacher::name = "小韬";
cout << p.TeachingTeacher::name << endl;
p.AdministrationTeacher::name = "小妍";
cout << p.AdministrationTeacher::name << endl;
p.TeachingTeacher::SpeakName();
p.AdministrationTeacher::SpeakName();
p.subject = "体育";
p.SpeakSubject();
p.job = "教导主任";
p.administration = "惩罚学生";
p.Execute();
p.Run();
//小韬
//小妍
//小韬
//小妍
//小韬
//小韬
//1
//体育
//教导主任执行惩罚学生
//跑步
#pragma endregion
}
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 785293209@qq.com

